Amazing Things to Know About Outsource Web Development
August 26, 2020
How To Discover And Fix Mixed Content Warnings On Https Sites
September 2, 2020What are the Isotopes in Chemistry?
Hello friends how are you all? Today we are going to talk about What are the Isotopes in Chemistry? Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in their nuclei. The word isotopes are derived from Greek (meaning equivalent places), which means the isotopes in the periodic table share the same location. Isotopes are described along with the volumes and weights. Isotopes are not really independent of amounts, but are just an associated property, like the color of a rock is an associated property of that rock.
Isotopes of a specific element have the same chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons. Isotopes of an element may be stable or radioactive. Radioactive isotopes emit radiations as they undergo radioactive decay and are transformed into new elements. Isotopes definition refers to elements with nuclei having the same number of protons but different neutron numbers so that the masses of contrasting isotopes vary between one and a few neutrons. Here is an example below of What are the Isotopes in Chemistry?
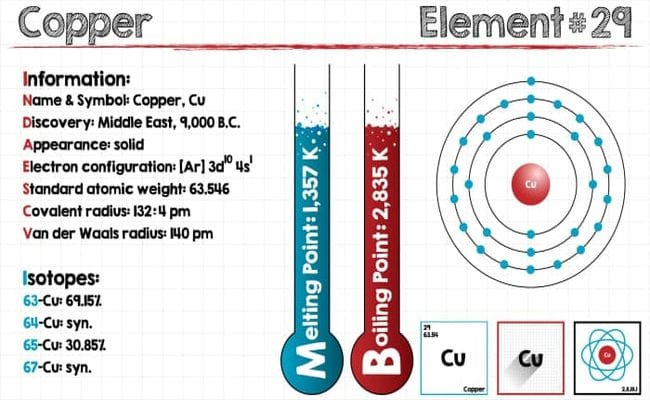
Isotopes of Copper
Copper is probably the most versatile metal in common use and its excellent conductivity is exploited in many lighting and other electrical appliances. Copper and its alloys are most extensively used among non-ferrous materials and occupy a second place among engineering materials. Copper is an unreactive metal and can be extracted from its ores using a reducing agent such as carbon. The copper which is extracted by this method contains impurities.
Atomic weight is an average because even atoms of the same element can vary. Many elements have two or more possible numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, and these alternate versions are called isotopes. Copper atomic number is 29. This is the atomic number which is the number of protons in the nucleus. Unless the atom is an ion, the atomic number also indicates the number of electrons. Some copper atoms have 34 neutrons while others have 36 neutrons. The copper atom with 36 neutrons adds more weight or mass to that atom’s nucleus than does the one with 34 neutrons but it does not affect the element’s chemical properties.
How Copper Behaves?
Our ancient ancestors recognized copper was different from iron. The two metals have different properties, because copper melted in their campfires, while iron required much hotter blazes. When exposed to water and air copper forms verdigris. Iron forms rust. After a while, an entire piece of iron can rust away, but copper will not.
Copper occurs in the form of ores containing sulfide, sulfates, silicates, oxides, and carbonates. The largest amount of copper is produced from sulfide ores such as chalcopyrite, chalcocite, and covellite. The ores are crushed and concentrated by floatation and other physical separation techniques. The concentrated ore is roasted in special furnaces to remove volatiles.
Copper and its alloys are most extensively used among non-ferrous materials and occupy a second place among engineering materials. Such popularity of copper is due to two of its important properties which are not possessed by steel. These properties are high electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Due to these unmatchable properties, copper cannot be substituted by steel.
Final Words.
So friends hope you will enjoy our article What are the Isotopes in Chemistry? and we hope that our article will help you. please give us your feedback in the comment.